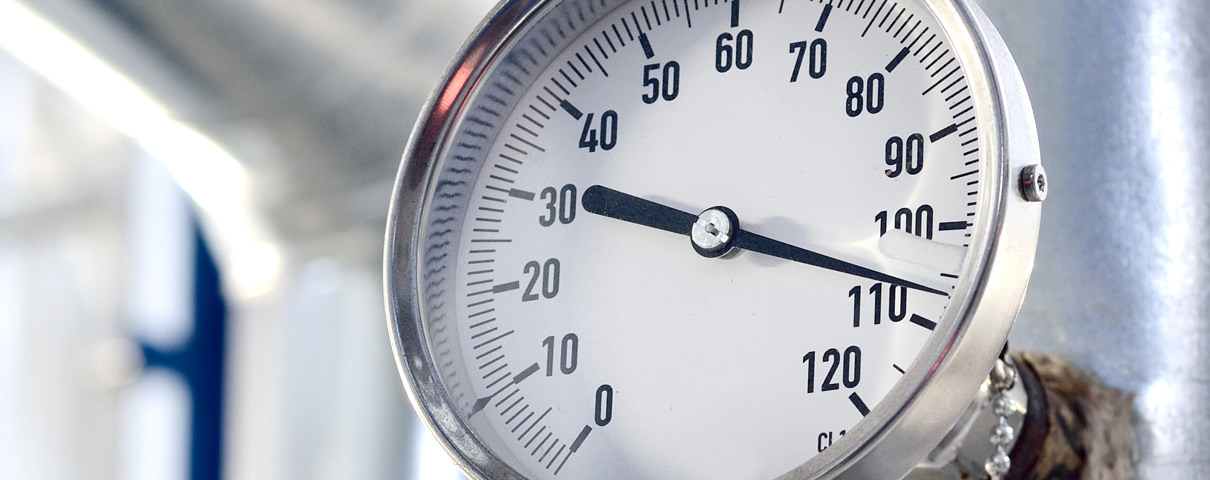
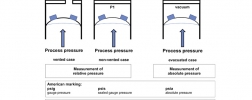
Electronic pressure sensors usually measure the change in pressure through the deformation of a diaphragm. If this diaphragm is exposed to the process pressure on one side and "vented" on the other side (and thus exposed to the ambient pressure), the deformation is …
Pressure
Fields of application for pressure sensors 2 – non-vented gauge pressure sensors: when unvented pressure sensors or transmitters are the best choice
Stefan HeuselIn most applications, gauge pressure measurement is required and therefore pressure sensors and pressure transmitters that measure pressure against the prevailing ambient pressure are commonly used for this. Those pressure sensors typically have a venting hole to …
Fields of application for pressure sensors 1 – vented gauge pressure sensors vs. absolute pressure sensors
Stefan HeuselThe user is often faced with the question: What kind of pressure sensor should I use - a relative/gauge or an absolute pressure sensor? From food processing to petrochemical plants, to plastic injection moulding and many other industrial applications, pressure …
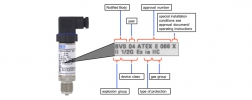
Marking of pressure sensors and transmitters according to ATEX Guideline 94/9/EC – how to read the ATEX label on pressure sensors
Stefan HeuselIf pressure sensors, pressure transmitters and other field equipment are used in the vicinity of flammable gases or dust, they may be subject to marking in accordance with the ATEX product guideline 94/9/EC. ATEX requires the type label of the sensor to include the …
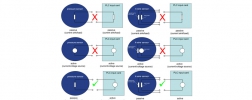
Electrical circuit for pressure sensors: when is a sensor active, and when passive?
Stefan HeuselWhen using pressure sensors, the output signals 0 … 20 mA, 4 … 20 mA and DC 0 … 10 V are frequently chosen in order for the sensor signals to be evaluated and further processed. For this, the signal output of the pressure sensor is usually connected to a …